German banks are facing challenges amid increasing corporate insolvencies and deteriorating credit ratings. Furthermore, low profitability has been a hurdle in recent years, as German banks are struggling to improve efficiency amid greater competition, as foreign banks such as ING have entered the market with low-cost online business models.
As part of the response to the COVID-19 pandemic, the German government, the European Commission and banking regulators have rolled out comprehensive fiscal support and regulatory forbearance measures to support corporates and private households. Going forward, sustainability of German banks would depend on how corporate and retail clients could benefit from these ad hoc support measures, and subsequently, the banks’ ability to refinance during stressed conditions. Nonetheless, German banks enjoy solid asset quality with a low non-performing loan ratio of ca. 1.3% at end-2020, one of the lowest in the eurozone. However, uncertainty of further consequences from the COVID-19 pandemic pose downside risks in the short term.
Low profitability due to structural weaknesses and negative interest rates
German banks had survived on razor-thin margins even before the pandemic, as the strong economic environment in the country was undermined by negative interest rates, high fragmentation of the sector, intense competition and vulnerable business models. Unlike foreign peers, they were unable to restructure their operations and diversify their products successfully. Cost control has been a challenge for German banks, as they have continued to underperform compared to European peers owing to high operating and legacy costs from exposure to the shipping industry. Moreover, investments to strengthen compliance and upgrade IT infrastructure continue to weigh on their efficiency.
German banks sit on a large pool of deposits and are dependent on interest income to a greater degree than other European banks. Moreover, increasing the share of fee income is difficult in a market where customers are accustomed to free basic banking services. In the current operating environment, implementation of efficiency measures and restructuring plans at German banks would be a challenge due to consistent public pressure to avoid layoffs during the crisis.
Corporates could face liquidity challenges in 2021
The containment measures in response to the pandemic resulted in a substantial drop in business activity of corporates, mainly those in contact-intensive sectors. Distancing measures and health concerns constrained hospitality and leisure services in particular. As per the World Travel & Tourism Council, Germany is likely to lose ca. EUR38bn owing to a significant decline in international tourists. Overall, turnover in the restaurant industry was 36% lower in 2020 compared to 2019. Manufacturing, though not directly impacted by the restrictions, witnessed a strong decline in activity owing to lower demand from both internal and external markets. Corporates are likely to face liquidity challenges in 2021 owing to sharp declines in revenue and cash flow. Nevertheless, according to the International Monetary Fund (IMF), the German economy is expected to grow by 3.6% in 2021 as vaccination accelerates. Faster growth in new orders from abroad has underpinned the German economic rebound in 2021, as reflected by growth in the manufacturing purchasing managers’ index (PMI). However, supply shortages for semiconductors and other intermediate goods due to supply chain disruptions caused by the COVID-19 pandemic continue to hold back production.
Increasing public debt levels pose downside risks
Bankruptcies could rise once the German government’s outstanding policy support measures—such as the insolvency moratorium, which has prevented a rise in bankruptcies—are rolled back. Debt of insolvent firms is likely to rise, although it is less pronounced compared to European peers’. The country could also witness an increase in personal bankruptcies due to rising unemployment. Nevertheless, the furlough scheme, known as Kurzarbeit (short-time work subsidy), contributed to Germany’s remarkable labour market resilience during the pandemic by preserving jobs and stabilising income. However, Kurzarbeit alone cannot completely address the labour market shock.
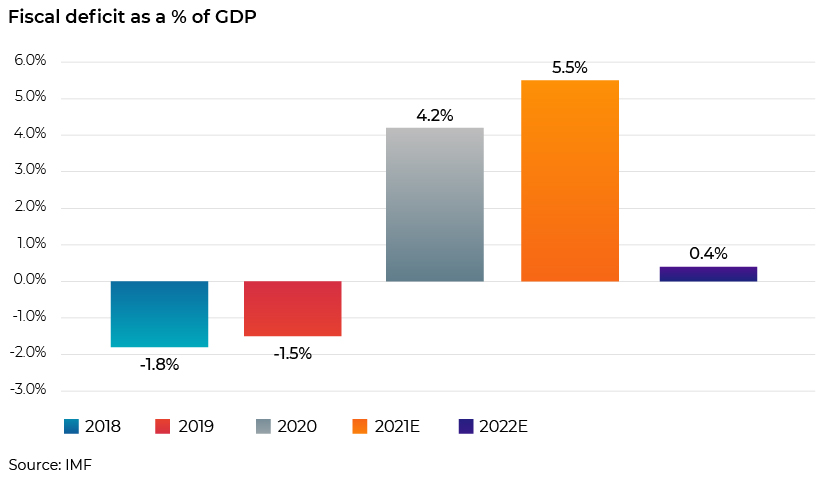
Germany’s public debt to gross domestic product (GDP) increased substantially to 68.9% in 2020 from 59.6% in 2019 due to the government’s unprecedented measures to fight the pandemic. According to the IMF, the ratio is expected to reach 70.3% and moderate to 67.3% in 2021 and 2022, respectively. As per the IMF, the fiscal deficit to GDP reached 4.2% in 2020 from a surplus of 1.5% in 2019. This is expected to increase further to a deficit of 5.5% in 2021 before recovering to only 0.4% in 2022. The government should continue with some direct support to viable firms that are key to the economy while assisting the exit of unviable ones. Going forward, lending conditions could tighten to prevent credit misallocation.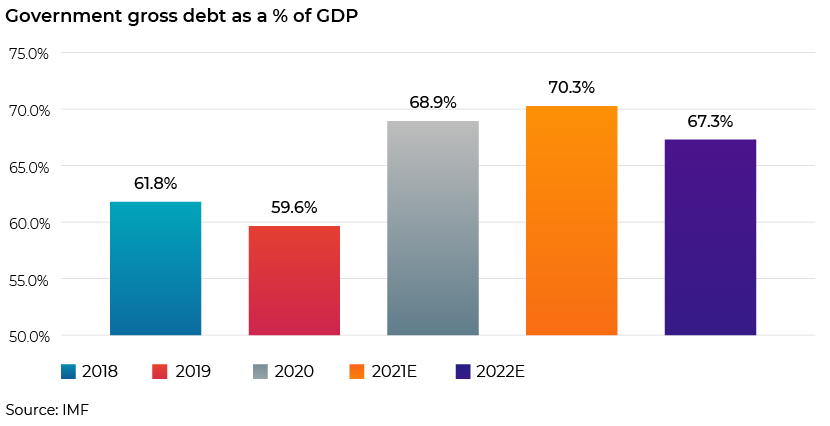
Increasing debt levels, coupled with lower cash flow generation of the corporates, could impact the asset quality of German banks. Nevertheless, German banks’ asset quality has been resilient, underpinned by conservative risk appetite, years of balance sheet clean-up and refocus on the domestic market. Moreover, German banks have strong capital buffers that should absorb short-term impacts on the asset quality. We further believe capital relief and restrictions on dividend payments should remain until economic recovery is sustainable.
