Why Solar Stocks and ETFs Are Up
Solar stocks and ETFs have been on a recent upswing, fueled by a positive development within the Chinese solar industry. The China Photovoltaic Industry Association (CPIA) took steps to address some key challenges facing the sector:
- Combating Price Wars: The CPIA called on its members to fight against "malicious low-price competition" that has driven down solar product prices. This initiative aims to create a more sustainable pricing environment for solar companies, potentially leading to healthier profit margins.
- Industry Consolidation: The CPIA also emphasized promoting mergers and restructurings within the solar sector. This could create stronger, more stable companies with better financial standing.
- Government Support and Stability: The CPIA is seeking government assistance in optimizing management policies and attracting new investment. Additionally, they highlighted the need to protect intellectual property rights and support advanced technologies. These initiatives could lead to a more stable and profitable domestic PV market in China, boosting investor confidence in the long-term growth of the solar industry.
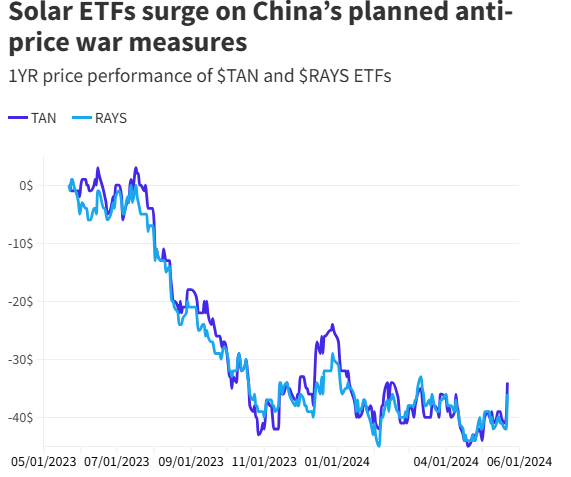
This news has been met with enthusiasm by investors. TAN (NYSE:TAN), the world's largest solar ETF, surged 9% on the news, while its smaller counterpart, TAYS (NASDAQ:RAYS), jumped 10%.
Another Factor Boosting U.S.-Based Solar Companies
U.S.-based solar companies have also seen a recent rise, fueled by a separate development. President Biden announced plans to increase tariffs on solar cells imported from China, raising them from 25% to 50%.
This move aims to address concerns that China has been using unfair practices to dominate the global solar supply chain. By making Chinese imports more expensive, the tariffs could benefit U.S.-based solar manufacturers, potentially giving them a competitive edge in the domestic market.
A breather for Solar ETFs after a challenging period
Solar stocks, once basking in the bright glow of stellar performance during the pandemic, have hit a rough patch over the past few years. This shift can be attributed to a confluence of factors creating a perfect storm.
Many solar companies are growth-focused, meaning their value is heavily tied to the expectation of future earnings. However, central banks have raised interest rates to combat post-Covid inflation. This has a double negative effect on solar stocks.
First, rising interest rates decrease the present value of those projected future earnings, making investors less enthusiastic. Second, for companies with significant debt burdens, higher interest rates translate to more expensive debt servicing, further squeezing profits and raising investor concerns about financial health.
Adding fuel to the fire, inflation throws another wrench into the equation. The rising cost of raw materials used in solar panel production, like polysilicon and silver, is putting a strain on profit margins. Companies are caught in a tightrope walk – either absorb these increased costs, impacting their bottom line, or pass them on to customers, potentially dampening demand for solar panels.
These combined factors – rising interest rates, inflation, and squeezed profit margins – have created a perfect storm for solar stocks, dimming their once-bright outlook.
Should you invest in Solar ETFs?
Investing in solar ETFs could potentially be a smart move due to the impressive growth and future potential of solar PV generation. In 2022, solar PV generation increased by a record 270 TWh, up 26%, reaching nearly 1,300 TWh – according to the IEA. This was the largest growth among all renewable technologies, even surpassing wind for the first time.
With continued economic attractiveness, supply chain development, and strong policy support from major regions like China, the United States, the European Union, and India, solar capacity is set to grow even more. Global investments in solar PV capacity rose by over 20% in 2022, surpassing USD 320 billion, and accounted for almost 45% of total global electricity generation investment.
This trend is expected to continue, making solar ETFs a promising investment with strong governmental and market backing.
How to Invest in Solar Stock with ETFs
U.S.-based investors can easily gain exposure to solar stocks via two pure-play Solar ETFs, TAN and RAYS.
Invesco Solar ETF (TAN) is the oldest and largest solar ETF, boasting over $1 billion in assets under management. The fund ETF tracks the MAC Global Solar Energy Index, investing in companies across the solar energy sector.
Another option is the U.S.-based Global X Solar ETF (RAYS) which tracks the Solactive Solar Index. RAYS invests in companies across the entire solar energy spectrum. This includes solar power production, integrating solar into energy grids, and even the development of solar-powered technologies like batteries.
Can European investors invest in Solar ETFs
Yes, European investors have options too. Invesco and Global X offer their counterparts, the Invesco Solar Energy UCITS ETF (LON:ISUN) (ISUN) and the Global X Solar UCITS ETF (ETR:RA7Z) (RA7Z), respectively.
How to Compare and Select Solar ETFs:
With multiple options available, selecting the right Solar ETFs for your portfolio requires careful consideration.
Here's a roadmap to guide you:
- Look at the Index: This is the blueprint. Some solar ETFs track indexes focused on established giants of the industry, offering stability but potentially slower growth. Others target indexes packed with high-growth, smaller players, promising faster returns but with increased volatility. Choose based on your risk tolerance and desired growth potential. However, not all ETFs track indexes! Some are actively managed, with portfolio managers making stock picks to potentially outperform the market. These come with higher fees and the risk of underperformance.
- Cost Control: Expense ratios, the annual fees of the ETF, can silently eat into your returns. Even a seemingly small difference can add up significantly over time. Compare the expense ratios of your shortlisted ETFs to keep more money working for you.
- Digging into Holdings: Don't settle for a black box. Investigate the specific companies each ETF holds. Does one focus heavily on a particular segment, like solar panel manufacturing or clean energy infrastructure? Does this alignment with a specific industry segment mesh with your investment goals?
- Liquidity Matters: Consider the trading volume, which reflects how many shares are bought and sold daily. A higher volume ETF generally translates to easier buying and selling at a fair price. Lower volume options might make entering or exiting your investment trickier, potentially impacting your ability to get your desired price.
While comparing ETFs can seem daunting, it can be a breeze with the right resources.