In our previous two-part series delving into the 2024 Trackinsight Global ETF Survey, we concentrated on revealing insights specific to thematic and active ETFs, providing a comprehensive overview of these popular segments of the ETF industry.
Today, we shift our focus to a steadily growing area of interest within the ETF landscape: Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) focused ETFs. As with the prior articles, my aim is to condense the essential findings into an easily digestible format, offering a snapshot of the prevailing trends and developments in ESG ETFs.
However, for a more thorough exploration of the survey's findings, I highly recommend diving into the full report, which is available for free download. Here are the main points you need to know when it comes to ESG ETFs in 2024.
ESG ETF AUM and options grew overall last decade
The landscape for ESG focused ETFs has seen remarkable growth, a trend underscored by the significant assets under management (AUM), which reached $550 billion by the end of 2023.
This expansion has been particularly notable during the pandemic years of 2020 and 2021, where the AUM surged by $335 billion, marking a 275% increase compared to the total AUM at the end of 2019.
From 2014 to 2023, the number of ESG ETFs available globally leaped from 148 to an impressive 1,826. This explosive growth in options for investors highlights the financial community's shifting focus towards sustainable investment practices.
The surge in interest and investment can be partially attributed to a keen focus on speculative clean energy themes, such as wind, solar, and hydro power.
However, the pandemic played a pivotal role in reshaping investor attitudes, propelling a more profound and conscious shift towards investments that not only promise returns but also align with broader societal and environmental objectives.
The global health crisis spotlighted the interconnectedness of health, economy, and the environment, urging investors to prioritize sustainability and governance in their portfolios more than ever before.
ESG ETF adoption varies between regions
Our analysis extends beyond the surface to uncover significant geographical disparities in the popularity and adoption of ESG ETFs.
European (EMEA) investors have consistently been at the forefront of embracing ESG ETFs, driven by robust legislative frameworks and a stronger cultural emphasis on sustainability.
By the end of 2023, Europe commanded nearly three-quarters of the global ESG ETF market with assets totaling $402 billion. This dominance is further illustrated by the growth within the EMEA region, where ESG ETFs expanded from 107 to 1,281 from 2014 to 2023.
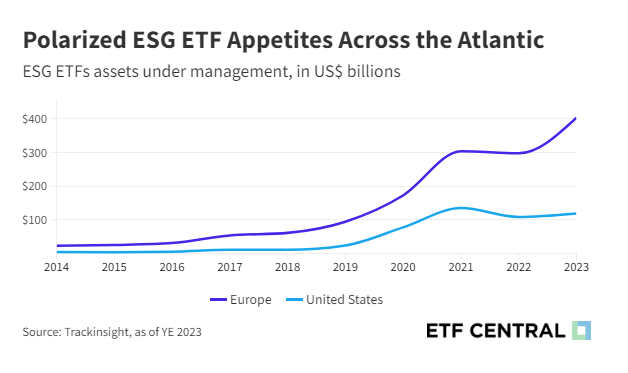
In comparison, North America’s ESG ETFs experienced growth from 34 to 430 over the same period, indicating a rising interest in sustainable investing, albeit at a pace slower than that of EMEA. Notably, the growth momentum in North America actually faced a slowdown in 2023, with merely 13 new ESG ETF launches observed throughout the year.
The disparity becomes even more pronounced when examining net inflows. In 2020, global net inflows into ESG ETFs reached $93 billion, peaking at $165 billion in 2021. During this zenith, the EMEA region contributed a substantial $109 billion in net flows, while North America also saw a significant uptick with approximately $51 billion.
However, North America's trajectory shifted markedly in the following years. By 2023, net flows not only receded but experienced a sharp reversal, with about -$1.31 billion of net outflows, in stark contrast to EMEA's continued growth, which saw nearly $50 billion in net inflows during the same period.
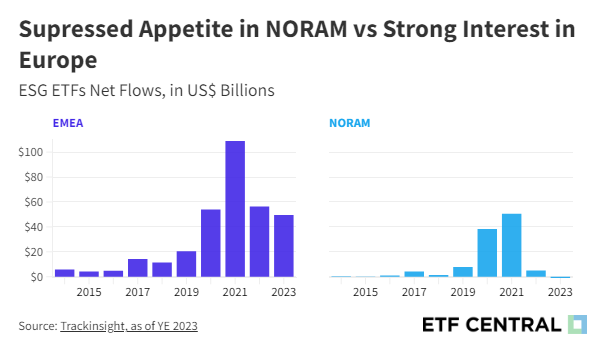
The lag in North America's ESG ETF momentum can primarily be attributed to anti-ESG legislation, largely spurred by political changes, conservative-led boycotts, and the emergence of a fringe "anti-ESG" movement.
Active ESG ETFs are becoming increasingly popular
While the majority of ESG investment strategies have traditionally been index-based, employing exclusionary criteria set forth by external organizations, a noticeable shift towards active management is emerging among investors.
This trend underscores a preference for investment firms that possess dedicated ESG expertise and adopt a more fundamental-driven approach to equity selection, rather than relying on the standard ESG frameworks offered by larger, more generalized firms.
A closer examination of North American ESG ETF flows in 2023 illuminates a distinct pattern: while passive funds witnessed $6.6 billion in outflows, indicative of a cooling interest, their active counterparts bucked the trend by drawing in $5.3 billion in new capital.
By the end of 2023, the landscape of ESG ETFs in NORAM had significantly evolved, with actively managed ETFs accounting for 13% of the total ESG ETFs AUM in the region. This marked a substantial increase from just 3% in 2018, highlighting the shifting preferences among ESG-focused investors towards active management.
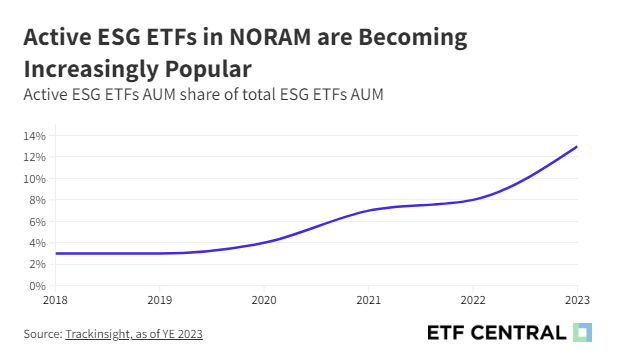
Active ESG investing extends beyond mere security selection; it encompasses a proactive engagement strategy with the companies in an ETF's portfolio. This "new active" style involves direct involvement in proxy voting and other forms of shareholder activism, aimed at driving positive change within the companies.
For instance, an actively managed ESG ETF might leverage its shareholder status to advocate for improved environmental practices, greater board diversity, or more transparent governance structures within its holdings.
This content was originally published by our partners at ETF Central.
